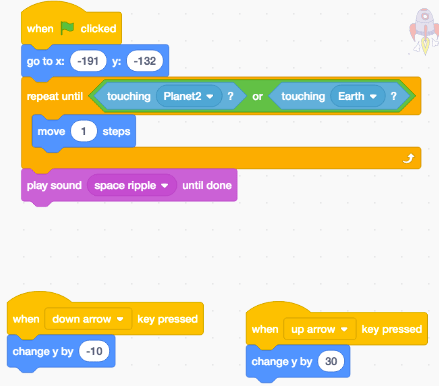
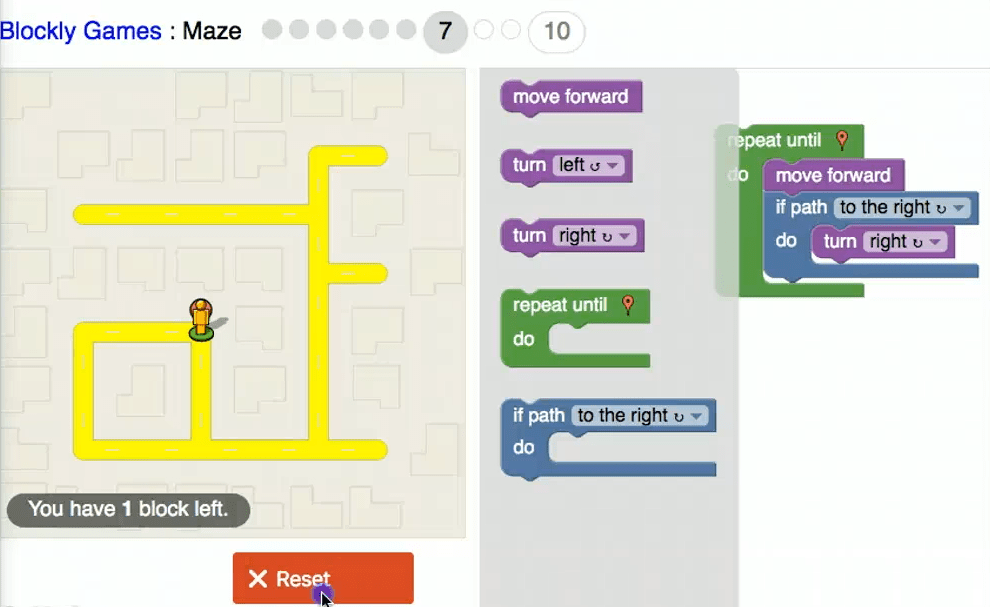
Constructionism in the classroom encourages and fosters student creativity and allows students to create and innovate. Constructionism is a pedagogical practice that can help students develop a large range of 21st century skills, they include, creativity, problem solving, critical thinking, inquiry, design thinking, collaboration, autonomy, literacy, numeracy, scientific understanding, digital literacy, communication, reflective learning capabilities and resilience.(Bower, Stevenson, Falloon, Forbes, & Hatzigianni, 2018).
There are many different technologies that allow for a constructionist approach in the classroom some of these technologies and applications include:
- LittleBits
- Makey Makey
- Chibi Lights
- Turing Tumble
- Neuron
- Circuitscribe
These different applications help students develop their 21st century skills from design to programming. When using these different programs it is important that students remain on-task, due to the high interactivity of constructivist classroom activities it is common that children go off task (Bower, et al., 2018). However this may contribute to children gaining a better understanding of the app through playing around or collaboration with classmates. While undertaking Constructionist activities students develop creativity, problem solving skills, critical thinking, inquiry capabilities, design thinking skills, collaborative skills, autonomy, literacy, numeracy, scientific understanding, technological capabilities, communication skills, reflective learning capabilities, and resilience, which are also important skills for the 21st century and students may benefit greatly for developing these traits (Bower, et al., 2018; Donaldson, 2014).
Furthermore, constructionist approaches in the classrooms, as outlined above, further foster creativity in students as it allows for them to explore and experiment with different technologies that are inherently creative. By students experimenting and playing with different applications they are able to for a proficiency that can be used to help teach other students and create a collaborative classroom. However it important to not use technology for the sake of using technology it is important for educators to apply the technology to achieve the learning outcomes for the area of study (Donaldson, 2014). Students through the use of technology in the classroom feel empowered by exploring and gaining a deeper understanding of particular applications, through which their creativity and self-confidence inflates (Donaldson, 2014).
References
Bower, M., Stevenson, M., Falloon, G., Forbes, A., & Hatzigianni, M. (2018). Makerspaces in primary school settings: advancing 21st century and STEM capabilities using 3D design and printing. Available at http://primarymakers.com
Donaldson, J. (2014). The Maker Movement and the rebirth of Constructionism. Hybrid Pedagogy. Available at: https://hybridpedagogy.org/constructionism-reborn/